Depth first search in short form DFS is a graph traversal algorithm. The time complexity of DFS is O(V+E) where V is the number of vertex and E is the number of edges.
Depth First Search (DFS) is a graph traversal algorithm that traverses a graph in depthward motion and uses a stack to remember to get back to its root. The algorithm starts at a given source node and visits as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. DFS can be implemented using both recursive and iterative approaches.
Depth First Search Algorithm
We will maintain a visited list and a stack
The algorithm works as follows
- We will start this algorithm by putting any nodes at the top of the stack.
- Take the top node from the stack let’s say it is r. Then add it to the visited list
- Traverse through the adjacency list of node r. If the adjacent node is not visited, put this node at the top of the stack
- Repeat 2 and 3 until the stack is empty
Here’s a high-level overview of how the recursive approach works:
- Create a visited set and mark all vertices as unvisited initially.
- Pick a starting vertex and call the recursive DFS function.
- In the recursive function, mark the current vertex as visited and print it.
- For each unvisited adjacent vertex, call the recursive function on it.
- Repeat step 4 until all vertices are visited.
Here’s a high-level overview of how the iterative approach works:
- Create a visited set and mark all vertices as unvisited initially.
- Pick a starting vertex and push it onto the stack.
- While the stack is not empty, pop a vertex and mark it as visited.
- Print the vertex.
- For each unvisited adjacent vertex, push it onto the stack.
- Repeat step 3 until the stack is empty.
DFS can be used for a variety of problems, such as finding connected components, detecting cycles, and solving puzzles like Sudoku.
Depth First Search Example
Let’s see how the Depth First Search algorithm works with an example. We use an undirected graph with 5 vertices.
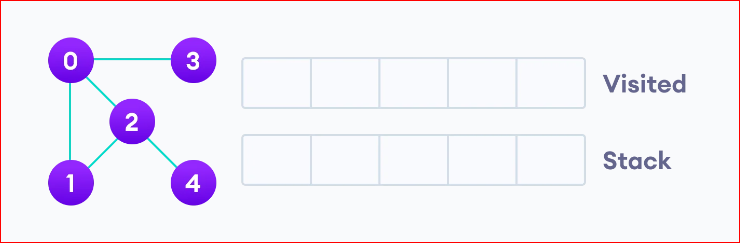
Start from node 0. Put 0 at the visited list and put all of it’s adjacent node to the stack.
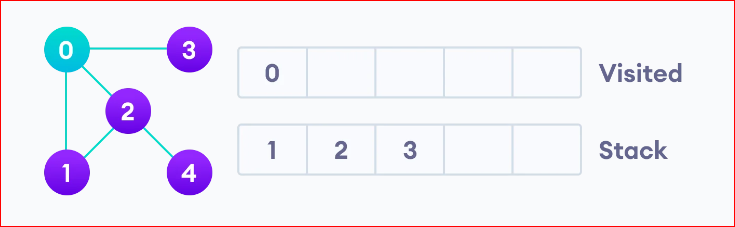
Next, we visit the element at the top of stack i.e. 1 and go to its adjacent nodes. Since 0 has already been visited, we visit 2 instead.
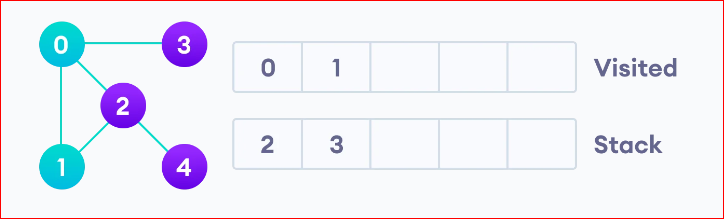
Vertex 2 has an unvisited adjacent vertex in 4, so we add that to the top of the stack and visit it.
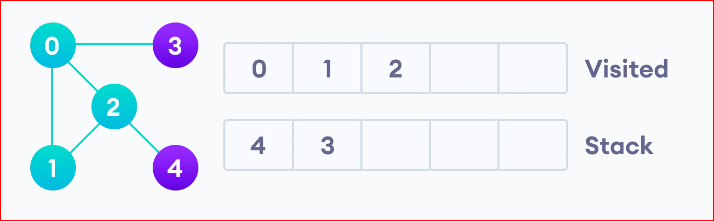
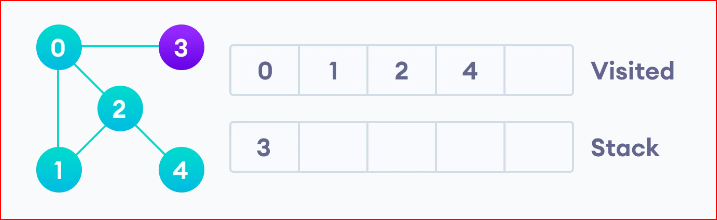
After we visit the last element 3, it doesn’t have any unvisited adjacent nodes, so we have completed the Depth First Traversal of the graph.

DFS Pseudocode (recursive implementation)
The pseudocode of the DFS recursive implementation is given below.
DFS(G, u)
u.visited = true
for each v ∈ G.Adj[u]
if v.visited == false
DFS(G,v)
init() {
For each u ∈ G
u.visited = false
For each u ∈ G
if u.visited==false
DFS(G, u)
}If the graph has more than one connected component then starting from a node will not visit all other nodes. So in the init function, we call dfs for every unvisited node.
DFS Implementation in Python
adj=[]
n=int(input()) # number of vertices.
m=int(input()) # number of edges
for i in range(n):
adj.append([])
# input edge list.
for i in range(m):
a, b=map(int, input().split())
adj[a].append(b)
adj[b].append(a)
visited=[]
for i in range(n):
visited.append(0)
def dfs(r):
global visited, adj
print(r)
visited[r]=1
for i in adj[r]:
if visited[i]==0:
dfs(i)
for i in range(n):
if visited[i]==0:
dfs(i)
This is a Python program for performing Depth First Search (DFS) traversal of an undirected graph, represented using adjacency list. Here is a brief explanation of the code:
The program starts by taking input of the number of vertices (n) and the number of edges (m) of the undirected graph.
An empty list ‘adj’ with n empty lists is initialized. This list will be used to store the adjacency list of each vertex.
The program then takes input of the edge list and updates the adjacency list accordingly. For each edge (a,b), it adds b to the adjacency list of a and a to the adjacency list of b.
An empty list ‘visited’ of size n with all elements set to 0 is initialized. The ‘visited’ list will be used to keep track of the vertices that have been visited during the DFS traversal.
A function ‘dfs’ is defined which takes a vertex ‘r’ as input and performs DFS traversal starting from that vertex. It first prints the vertex ‘r’ and sets the corresponding element in the visited list to 1. Then, for each adjacent vertex ‘i’ of ‘r’, if it hasn’t been visited yet, it calls the dfs function recursively with ‘i’ as input.
The program then iterates over all vertices and calls the dfs function for any vertex that hasn’t been visited yet.
DFS Implementation in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int> > adj;
vector<int> visited;
void dfs(int r)
{
visited[r]=1;
cout<<r<<endl;
for(auto it:adj[r])
{
if(visited[it]==0)
{
dfs(it);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n; // n is the number of vertices
cin>>m; // m is the number of edges
adj.resize(n); // n vector for each node
// input edgelist
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int a, b;
cin>>a>>b;
adj[a].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a);
}
visited.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(visited[i]==0)
{
dfs(i);
}
}
return 0;
}
This is a C++ code for Depth First Search (DFS) on an undirected graph, which is similar to the Python code provided earlier.
Here’s a brief explanation of the code:
adj is a vector of vectors which represents the adjacency list of the graph. Each vector adj[i] represents the list of vertices adjacent to the i-th vertex.
visited is a vector that keeps track of whether a vertex has been visited or not. Initially, all vertices are marked as unvisited (0).
dfs function takes an integer r as input which represents the vertex to start the DFS from. It first marks the current vertex as visited and prints its value. It then recursively calls dfs on all unvisited adjacent vertices of the current vertex.
In the main function, we first input the number of vertices n and edges m. We then resize the adjacency list and visited vectors to size n. We then input the edge list and populate the adjacency list. Finally, we iterate over all vertices and call the dfs function on each unvisited vertex to ensure all vertices are visited.
Note: This code assumes that the vertices are numbered from 0 to n-1. If the vertices are numbered differently, some adjustments may be required in the code.



