An adjacency list represents a graph as an array of linked lists. The index of the array represents a vertex and each element in its linked list represents the other vertices that form an edge with the vertex.
For example, We have a graph below
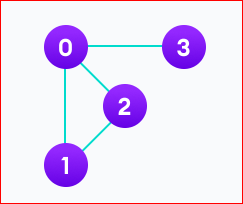
We can represent this graph in a link list like below
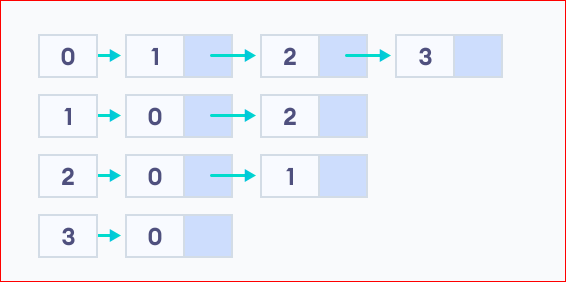
Here 0 has edges with 1, 2, and 3. 1, 2, and 3, are adjacent to 0.
thus 0 and 2 are adjacent to 1
0 and 1 are adjacent to 2
0 is adjacent to 3
Adjacency List C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n; // n is the number of vertices
cin>>m; // m is the number of edges
vector<vector<int> > adj(n); // n vector for each node
// input edgelist
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int a, b;
cin>>a>>b;
adj[a].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<i<<": ";
for(auto it:adj[i]) cout<<it<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Adjacency List Python
adj=[]
n=int(input()) # number of vertices.
m=int(input()) # number of edges
for i in range(n):
adj.append([])
# input edge list.
for i in range(m):
a, b=map(int, input().split())
adj[a].append(b)
adj[b].append(a)
for i in range(n):
print(i, end=': ')
for j in adj[i]:
print(j, end=' ')
print('')



